Duration 4:36
The Uterus, Location, Anatomy and Function
Published 13 Feb 2021
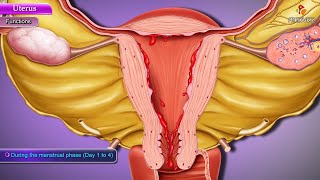
. Chapters 0:00 Introduction 0:58 Location of the Uterus 1:49 Anatomy of the Uterus 3:45 Function of the Uterus Womb" and "In utero" redirect here. For other uses, see Womb (disambiguation). For the album by Nirvana, see In Utero. "Hystera" and "Uterine" redirect here. For the state of mind, see Hysteria. For siblings with the same mother but different fathers, see Uterine siblings. Uterus Image showing different structures around and relating to the human uterus. Details Precursor Paramesonephric duct System Reproductive system Artery Ovarian artery and uterine artery Vein Uterine veins Lymph Body and cervix to internal iliac lymph nodes, fundus to para-aortic lymph nodes, lumbar and superficial inguinal lymph nodes. Identifiers Latin uterus Greek ὑστέρα (hystéra) Anatomical terminology [edit on Wikidata] Different regions of Uterus displayed & labelled using a 3D medical animation still shot Different regions of Uterus displayed & labelled using a 3D medical animation still shot The uterus (from Latin "uterus", plural uteri) or womb (/wuːm/) is a major female hormone-responsive secondary sex organ of the reproductive system in humans and most other mammals. Things occurring in the uterus are described with the term in utero. In the human, the lower end of the uterus, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the upper end, the fundus, is connected to the fallopian tubes. It is within the uterus that the fetus develops during gestation. In the human embryo, the uterus develops from the paramesonephric ducts which fuse into the single organ known as a simplex uterus. The uterus has different forms in many other animals and in some it exists as two separate uteri known as a duplex uterus. In medicine, and related professions the term uterus is consistently used, while the Germanic-derived term womb is commonly used in everyday contexts.
Category
Show more
Comments - 6














![Moia File Virus Ransomware [.moia Removal and Decrypt] .moia Files](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/qoE7VSjFgvw/mqdefault.jpg)